Table of Contents
A recent groundbreaking study has exposed over 100 LTE and 5G network security flaws, shaking the foundations of modern cellular technology.
LTE and 5G Network Security Flaws Discovered in Major Study
Researchers from the University of Florida and North Carolina State University uncovered vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to disrupt city-wide cellular communications, monitor user data, and exploit the core cellular network.
The study, aptly titled “RANsacked: A Domain-Informed Approach for Fuzzing LTE and 5G RAN-Core Interfaces”, offers alarming insights into the security gaps plaguing LTE and 5G implementations.
Key Takeaway to LTE and 5G Network Security Flaws
- LTE and 5G Network Security Flaws: The discovery of over 100 flaws highlights the urgent need for stronger safeguards in LTE and 5G technologies.
What the Study Revealed
The researchers identified 119 vulnerabilities spread across both LTE and 5G implementations. These vulnerabilities are categorized under two main attack types:
- Attacks by Unauthenticated Devices
- These flaws enable any mobile device, even without a SIM card, to disrupt services like calls, texts, and data across an entire city.
- Exploits via Compromised Base Stations
- By taking over base stations or femtocells, attackers could gain deeper access to the cellular core network and carry out large-scale attacks.
| LTE Implementations | 5G Implementations | Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Open5GS | Open5GS | 119 vulnerabilities |
| Magma | Magma | 97 unique CVEs |
| OpenAirInterface | OpenAirInterface | Critical risks |
The affected systems include popular implementations like Open5GS, Magma, Athonet, SD-Core, srsRan, and NextEPC.
The Nature of the Threat
One startling revelation was the ease of exploiting these vulnerabilities.
Researchers demonstrated that sending a single small data packet could crash critical components like the Mobility Management Entity (MME) in LTE networks or the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) in 5G systems.
- Buffer Overflows: A common vulnerability where attackers overload memory systems to gain unauthorized access.
- Memory Corruption Errors: These errors can be exploited to access sensitive user data and track subscriber locations.
Understanding the Two Threat Models Behind LTE and 5G Vulnerabilities
Researchers categorized the discovered vulnerabilities into two primary threat models, each highlighting different avenues for exploitation:
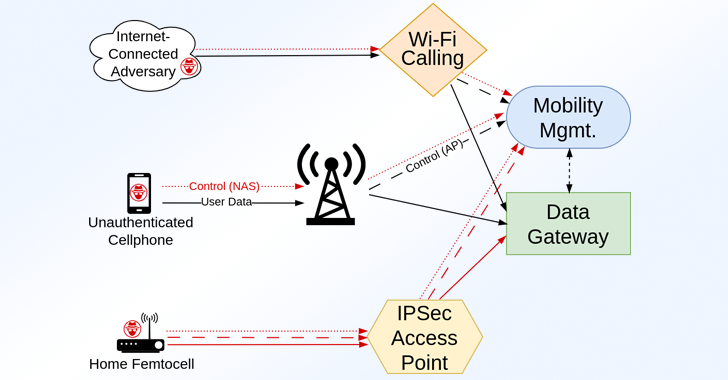
1. Exploitation via Unauthenticated Mobile Devices
This threat model involves attackers using mobile devices that do not require valid SIM cards.
These devices can exploit the vulnerabilities by sending specifically crafted malformed packet sequences at the start of a cellular connection.
Traditionally, such attacks were limited to devices within radio proximity to the LTE/5G core under attack.
However, the landscape has changed with the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi Calling services. These services enable attackers from any location with internet access to execute the same exploits.
This eliminates the need for specialized equipment like Software-Defined Radios (SDRs), significantly broadening the attack scope.
2. Exploitation via Base-Station Access
The second threat model involves attackers gaining direct access to a cellular core through base stations or femtocells. There are two common scenarios for this:
- Compromised Base Stations/Femtocells: Many cellular providers distribute home or office femtocell devices to boost signals. These devices function as base stations, making them vulnerable targets. Adversaries can gain persistent physical access to these devices, allowing them to extract sensitive data such as IPsec keys through techniques like memory dumps.
- Network Misconfigurations or Key Leaks: Attackers can also infiltrate the IPsec network used by base stations to communicate with the cellular core due to misconfigurations or leaked cryptographic keys.
The increasing deployment of smaller and more accessible 5G base stations in urban and suburban areas further exacerbates this threat, as these installations are often easier to physically access compared to traditional large towers.
These threat models underline the critical need for enhanced security measures to protect LTE and 5G networks from evolving vulnerabilities.
Real-Life Implications
The vulnerabilities in LTE and 5G networks are not merely theoretical risks but have tangible and alarming real-world consequences.
A security flaw highlighted on March 7, 2018, sheds light on how 4G LTE security flaws could be exploited to send false emergency alerts to mobile phones, causing widespread panic.
Researchers from Purdue University and the University of Iowa identified these vulnerabilities, which could also enable attackers to snoop on messages, track locations, and carry out at least nine other types of attacks.
Their study introduced a tool designed to detect such flaws.
Key Details About the 2018 Incident:
- Exploits Enabled: Phony emergency alerts, unauthorized location tracking, and disruption of cellular services.
- Root Cause: Dependence on temporary identifiers in LTE networks, which were neither truly temporary nor random.
- Industry Response: The discovery prompted carriers to begin addressing these vulnerabilities.
Why These Security Flaws Matter
The introduction of 5G has brought innovative technologies like home-use femtocells and gNodeB base stations.
However, these advances also open doors for physical and remote attacks. Without proper safeguards:
- City-Wide Disruptions: Entire cities could lose cellular services.
- Subscriber Data Leaks: Attackers could access call and location data.
- Targeted Attacks: High-profile individuals or businesses could be targeted.
How the Vulnerabilities Were Found
Using a fuzzing tool called RANsacked, researchers tested Radio Access Network (RAN)-Core interfaces, exposing systems that were previously assumed secure.
The results prove that even high-tech 5G systems are vulnerable without additional security measures.
Forecast: The Future of LTE and 5G Security
As 5G continues to expand, more devices will connect to cellular networks, increasing potential attack surfaces. If vulnerabilities remain unaddressed:
- Cybersecurity spending on mobile networks will surge.
- Companies will adopt AI-driven security systems to detect and mitigate threats faster.
- Regulatory bodies may enforce stricter security compliance for cellular providers.
About the Researchers
This study was conducted by experts at the University of Florida and North Carolina State University, both renowned for their contributions to cybersecurity and telecommunications research.
Rounding Up
The discovery of over 100 LTE and 5G network security flaws underlines the need for urgent action. Cellular providers, governments, and cybersecurity professionals must collaborate to strengthen security protocols and ensure safer networks for everyone.
FAQs
What are the main LTE and 5G network security flaws?
- They include vulnerabilities like buffer overflows, memory corruption, and issues with unauthenticated access.
How were these flaws discovered?
- Researchers used a fuzzing tool called RANsacked to expose vulnerabilities in LTE and 5G network implementations.
What can be done to address these issues?
- Cellular providers can update systems, implement stricter security protocols, and adopt AI-driven detection methods.
Why is this discovery significant?
- It highlights the risks of large-scale cellular disruptions and user data breaches in modern communication systems.
Is my data safe on LTE and 5G networks?
- While providers are improving security, the discovery of these flaws shows that risks still exist.





