Table of Contents
Hackers Deceive Android Users by Exploiting WebAPK with Malicious Apps: Hackers are exploiting Android’s WebAPK technology to deceive Android users into unknowingly installing malicious web apps. By impersonating legitimate applications, threat actors can capture sensitive personal information from unsuspecting victims.
This article explores the attack method and the use of specialized device spoofing tools in the cybercriminal landscape.
Key Takeaways to Hackers Deceive Android Users by Exploiting WebAPK with Malicious Apps:
- Threat actors are leveraging Android’s WebAPK technology to trick users into installing malicious web apps.
- A recent attack impersonated PKO Bank Polski, a multinational banking company, to deceive victims.
- Cybercriminals are utilizing specialized device spoofing tools to bypass anti-fraud controls and impersonate compromised account holders.
Cybercriminals have discovered a way to exploit Android’s WebAPK technology, tricking Android users into unwittingly installing malicious web applications.
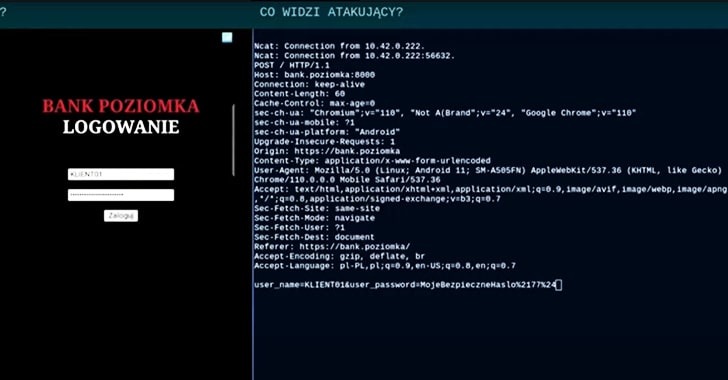
In a sophisticated attack, victims receive SMS messages prompting them to update their mobile banking application.
The provided link leads to a website that utilizes WebAPK technology to install a malicious app on the victim’s device. By impersonating reputable organizations such as PKO Bank Polski, attackers can capture sensitive personal information from unsuspecting users.
Understanding WebAPK Technology and Attack Methodology
WebAPK is an Android feature that enables users to install progressive web apps (PWAs) directly to their home screens, bypassing the need for the Google Play Store. Google Chrome’s minting server generates and signs an APK for the PWA, allowing for a seamless installation process.
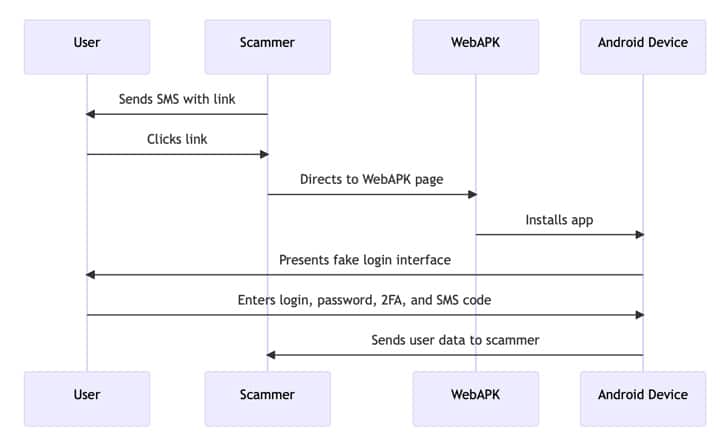
Exploiting this technology, hackers create fake banking apps, such as “org.chromium.webapk.a798467883c056fed_v2,” which prompt users to enter their login credentials and two-factor authentication tokens.
Unfortunately, victims unknowingly provide this information, resulting in the theft of their sensitive data.
Challenges and Recommendations for Mitigation
Countering these attacks presents challenges, as WebAPK applications generate different package names and checksums on each device. This dynamic nature makes it difficult to use these parameters as Indicators of Compromise (IoC).
To mitigate such threats, it is advisable to block websites that employ the WebAPK mechanism to carry out phishing attacks. By implementing measures to prevent access to these sites, users can reduce the risk of falling victim to such deceptive schemes.
The Rise of Specialized Device Spoofing Tools in Cybercriminal Activities
In parallel to the WebAPK exploitation, cybersecurity researchers have discovered the increasing use of specialized device spoofing tools by cyber criminals.
These tools, marketed on the dark web, enable threat actors to impersonate compromised account holders and bypass anti-fraud controls. Specifically, tools like Enclave Service and MacFly can spoof mobile device fingerprints, software information, and network parameters, evading detection by anti-fraud systems.
Cybercriminals leverage these tactics, along with banking malware like TimpDoor and Clientor, to conduct unauthorized transactions and exploit weak fraud controls.
Conclusion
The exploitation of Android’s WebAPK technology by hackers highlights the importance of remaining vigilant against evolving cyber threats.
Users must exercise caution when prompted to update applications through unfamiliar channels, especially in the case of financial applications. Blocking websites that employ the WebAPK mechanism can add an additional layer of protection against phishing attacks.
Moreover, the emergence of specialized device spoofing tools underscores the need for robust anti-fraud measures to combat the impersonation of compromised account holders. By staying informed and implementing effective security measures, individuals and organizations can better defend against these malicious activities.