Table of Contents
Ukrainian Minors Recruited for CyberEspionage: The recruitment of Ukrainian minors for cyber espionage amid Russian airstrikes sheds light on the alarming tactics used in modern warfare.
A shocking investigation by the Security Service of Ukraine (SSU) has uncovered how Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB) exploits children as young as 15 to gather intelligence and support airstrikes in Ukraine.
These revelations highlight a disturbing new front in the ongoing conflict.
Key Takeaway to Ukrainian Minors Recruited for CyberEspionage:
- Ukrainian Minors Recruited for CyberEspionage: Ukrainian minors recruited for cyber espionage reveal the evolving tactics of warfare used by Russia’s FSB.
What Did the Investigation Reveal?
The SSU’s recent operation in Kharkiv unveiled a disturbing espionage campaign orchestrated by the FSB. The agency arrested two groups of minors, aged 15 and 16, accused of performing tasks that included:
| Task | Details |
|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | Taking photos/videos of sensitive targets. |
| Arson | Setting fires to specific locations. |
| Target Identification | Sharing geographical data of air defense sites. |
The children, unaware of the full implications, were lured into these activities under the guise of participating in “quest games.”
How Were the Minors Recruited?
The FSB used clever tactics to recruit these minors:
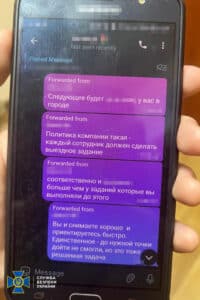
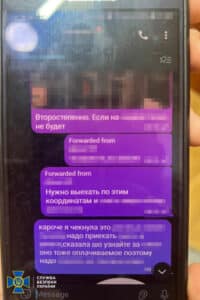
- Gamification: The “quest games” required the children to visit specific locations, record observations, and submit the data online.
- Anonymous Chats: Recruits shared their findings through encrypted messaging platforms to avoid detection.
- Covert Operations: Separate cells operated independently, making it harder for law enforcement to connect the dots.
This data was later used to coordinate airstrikes in Kharkiv, resulting in devastating consequences for local communities.
Who Was Behind the Operation?
The investigation led to several arrests:
- Organizers Detained: The SSU captured all members of the cells, with one organizer now facing life imprisonment.
- Russian Police Officer Implicated: A police officer from Krasnodar, Russia, acted as a liaison for these groups. He has been charged in absentia for sabotage under Ukraine’s martial law.
A Broader Cyber Threat
While the SSU’s operation focused on physical sabotage, Ukraine’s Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UA) has reported increased cyberattacks targeting defense companies and security forces.
These attacks, attributed to the Russia-linked group UAC-0185, showcase how traditional espionage is now intertwined with digital warfare.
Real-Life Example
This isn’t the first time children have been used in military operations. In 2020, a similar case emerged where minors were tricked into spreading misinformation during protests in Belarus.
Why Is This Concerning?
Using minors in espionage is a violation of international laws and puts children directly in harm’s way. It also raises ethical concerns about the long-term psychological effects on those coerced into these operations.
For Ukraine, these tactics represent an evolving and insidious form of warfare that targets not just military but also civilian structures.
About the Security Service of Ukraine (SSU)
The Security Service of Ukraine is the country’s principal intelligence agency, tasked with counterintelligence, counterterrorism, and cybersecurity. Learn more about the SSU on their official website.
Rounding Up
The recruitment of Ukrainian minors for cyber espionage amid Russian airstrikes reveals how conflicts are shifting into darker, more insidious territories.
As the SSU continues its efforts to thwart these operations, the global community must remain vigilant against similar tactics being deployed elsewhere.
FAQs
What is the SSU?
- The Security Service of Ukraine is responsible for countering espionage, sabotage, and terrorism.
Why are minors targeted in these operations?
- Minors are often seen as less suspicious and easier to manipulate, making them prime targets for covert activities.
What is a “quest game” in this context?
- A quest game is a cover used by the FSB to disguise espionage tasks as harmless challenges for children.
How can civilians protect themselves from similar schemes?
- Educating communities about these tactics and monitoring online interactions are crucial steps in prevention.
Are there international laws protecting minors in war?
- Yes, international conventions like the Geneva Conventions explicitly prohibit the use of children in armed conflicts.
This news item aims to keep you informed and aware of the evolving nature of cyber and physical warfare. Stay updated with more insights into cybersecurity and geopolitical developments.