Table of Contents
Fake Video Apps Threaten Web3 Users: Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a disturbing trend where fake video apps are threatening Web3 users. These deceptive apps are being used to steal sensitive data from professionals in the cryptocurrency and blockchain sectors. Hackers disguise the apps as legitimate video conferencing tools, luring victims into downloading malware under the pretense of business meetings.
This latest scam highlights how creative cybercriminals are becoming, leveraging sophisticated techniques to target unsuspecting users. If you’re involved in the Web3 space, this is a wake-up call to prioritize your security.
Key Takeaway
Fake Video Apps Threaten Web3 Users: Always verify the authenticity of video conferencing apps to protect your data.
How Fake Video Apps Threaten Web3 Users
Hackers have launched a campaign, codenamed Meeten, where they pose as representatives of fake companies to trick Web3 professionals.
These attackers use AI-generated websites to appear credible and approach victims through Telegram, offering lucrative business opportunities.
Victims are directed to download fake apps like Meeten, Meetone, Meetio, Clusee, and Cuesee. Once installed, these apps execute malware called Realst to steal sensitive data.
The Techniques Hackers Use
Here’s how these scams typically work:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Contact | Hackers reach out via Telegram, pretending to discuss investment deals or partnerships. |
| Fake App Setup | Users are directed to download a video conferencing app from a fake website. |
| Data Theft | Malware collects cryptocurrency wallet data, Telegram credentials, browser cookies, and more. |
| Final Exploitation | The stolen information is sent to the attacker’s server for misuse. |
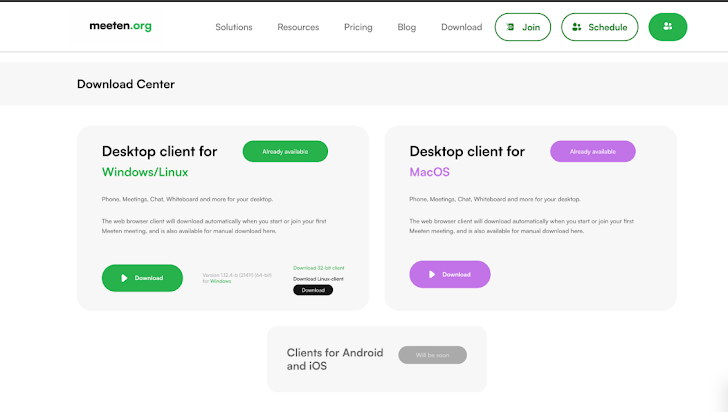
The Malware in Action
The macOS version of this malware presents a fake error message, asking users to enter their system password. This tactic has been used by other malware, including Atomic macOS Stealer and MacStealer.
The malware targets popular browsers like Google Chrome, Brave, and Vivaldi, along with cryptocurrency wallets and iCloud Keychain data. A similar attack was reported earlier this year, involving a fake site called meethub.gg.
Why This Threat Is Growing
According to Cado Security, hackers increasingly use AI to build realistic websites, making scams harder to detect. These websites can appear convincing, complete with professional logos, content, and branding.
Past campaigns, like one involving the Markopolo malware in June 2024, also targeted crypto users with fake meeting software. Such attacks show how cybercriminals adapt their strategies to exploit vulnerabilities in new technologies.
How to Stay Safe
Here are practical steps to protect yourself if fake video apps threaten Web3 users:
- Verify App Sources: Only download video conferencing apps from official websites or trusted app stores.
- Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Offers: Avoid deals that seem too good to be true, especially from unknown contacts on Telegram.
- Use Antivirus Software: Invest in reliable antivirus programs to detect and block malware.
- Regularly Update Your System: Keep your operating system and apps updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
About Cado Security
Cado Security is a leading cybersecurity company specializing in cloud threat intelligence. Their expertise helps businesses detect and mitigate advanced cyber threats.
Rounding Up
As hackers refine their tactics, Web3 users must stay vigilant. The discovery that fake video apps threaten Web3 users underscores the importance of securing your digital activities.
By taking proactive measures like verifying app sources and enabling two-factor authentication, you can protect your assets and reputation in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
By staying informed and cautious, you can outsmart hackers and keep your digital assets safe.
FAQ to Fake Video Apps Threaten Web3 Users
What are fake video apps?
Fake video apps are malicious software disguised as legitimate conferencing tools. They are used to steal sensitive information.
Who is being targeted by these scams?
The primary targets are Web3 professionals, cryptocurrency traders, and blockchain developers.
How can I identify a fake video app?
Check the app’s source, reviews, and website. Avoid downloading apps from unknown platforms.
What should I do if I suspect an app is fake?
Immediately uninstall the app and run a malware scan on your device.
Can antivirus software help?
Yes, antivirus software can detect and block malware before it compromises your data.
Are macOS users more at risk?
Both macOS and Windows users are targeted, but macOS users face unique tactics like password-stealing scripts.
How can I report such scams?
You can report scams to platforms like Telegram and cybersecurity organizations like Kaspersky.





