Table of Contents
MFA LockBit Ransomware Prevention should be critically looked at for many users underestimate the importance of Multi-Factor Authentication in safeguarding against sophisticated threats like LockBit.
This advanced ransomware can compromise your systems swiftly, making it crucial for you to implement stronger security measures. MFA adds an extra layer of protection, requiring more than just your password to access sensitive information.
For a real-world example of how LockBit is targeting educational institutions, check out this insightful article on LockBit 3.0 Ransomware Targets Schools.
You can significantly reduce your risk by utilizing MFA in your security protocols.
Key Takeaways to MFA LockBit Ransomware Prevention:
- Enhanced Security: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds ‘an additional layer of security beyond just passwords, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Reduction of Attack Surface: Implementing MFA minimizes the risk of credential theft, as it requires users to verify their identity through multiple methods, reducing the opportunity for LockBit attacks to succeed.
- Adaptability to Threats: MFA can adapt to different threats, enabling organizations to stay one step ahead of evolving ransomware tactics, such as those employed by LockBit.
Understanding LockBit Attacks
A LockBit attack involves a form of ransomware designed to encrypt your files and demand a ransom for their release.
This specific strain has evolved to exploit vulnerabilities in organizations, rendering standard security protocols insufficient.
For comprehensive insights on this threat, check out Surviving LockBit: How to Protect Your Organization.
Overview of LockBit Ransomware
Against a backdrop of rising cyber threats, LockBit ransomware stands out for its automation and speed, quickly entering your systems to encrypt vital data and demanding payment, often within hours.
Recognizing the signs and understanding their mechanisms is imperative for defending your organization.
Attack Vectors and Targeted Industries
By targeting weaknesses in various sectors, LockBit employs multiple attack vectors, including phishing emails, unsecured RDP connections, and extensive network scans.
These methods often lead to devastating impacts, particularly for sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, where downtime can result in significant losses.
Also, knowing the industries most affected by LockBit can help you understand your organization’s vulnerability.
Cybercriminals often focus on imperative services, aiming to cause maximum disruption and increase the likelihood of receiving payment.
By analyzing attack vectors, you can better prepare and strengthen your defenses against these sophisticated threats.
The Concept of Multi-Factor Authentication
If you want to strengthen your security posture, understanding multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to sensitive systems or information.
By implementing this layered approach, you significantly reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
Definition and Components
On its most basic level, multi-factor authentication combines something you know (like a password), something you have (such as a smartphone), and something you are (biometric data).
These three components work together to ensure that access is granted only to authorized individuals, making it much harder for cybercriminals to infiltrate your accounts.
How MFA Works to Enhance Security
Above all, MFA enhances your security by adding barriers that adversaries must breach. When you attempt to log in, you enter your password and then are prompted to provide a second factor, such as a code sent to your mobile device.
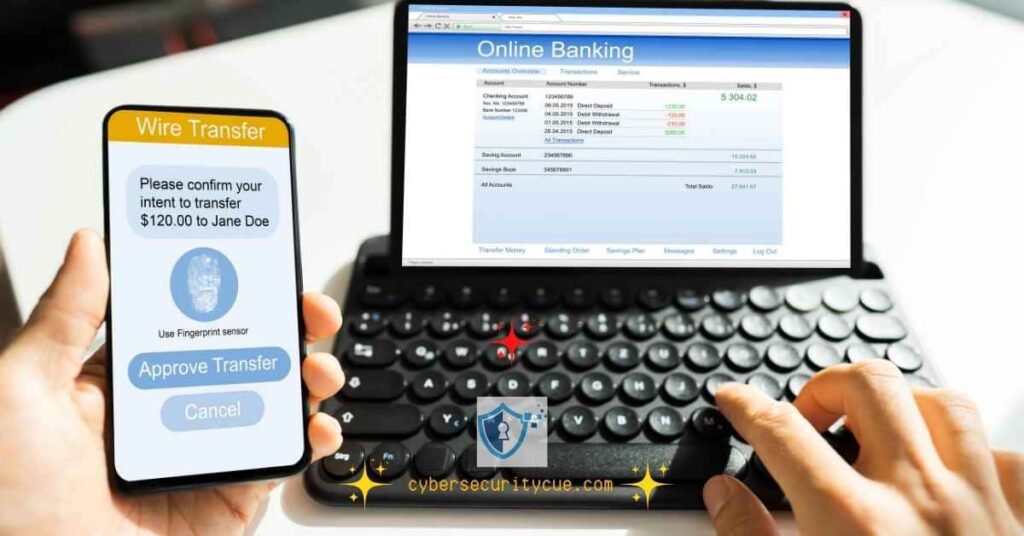
This additional step ensures that even if someone gets hold of your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor.
Components of MFA work in tandem to provide a robust defense against unauthorized access. By necessitating multiple verification forms, you make it much more difficult for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
Even if a malicious actor manages to steal your password, without your mobile device or biometric data, they will find it nearly impossible to gain entry.
This layered security not only deters attacks but also provides peace of mind that your sensitive information remains protected.
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication Against Ransomware
Once again, it is evident that multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as a powerful deterrent against ransomware attacks, like those from LockBit.
By requiring multiple verification methods before granting access, MFA significantly hampers a hacker’s ability to infiltrate your systems, making it harder for them to deploy malicious software or steal sensitive data.
Reducing Unauthorized Access
Above all, MFA helps reduce unauthorized access to your accounts. By implementing multiple layers of verification, you ensure that even if a password is compromised, an attacker still faces additional barriers, effectively slowing them down and minimizing their chances of success.
Diversifying Security Measures
For effective defense, diversifying your security measures is crucial. Relying solely on passwords is inadequate; incorporating MFA alongside firewalls, anti-virus software, and regular software updates creates a multi-layered security strategy that is hard for cybercriminals to bypass.
For instance, using a combination of MFA and other security protocols not only strengthens your overall defenses but can also discourage attackers.
When they encounter a robust security framework that includes various protective measures, they are less likely to target your system, as the effort required to breach your defenses becomes too great.
This layered approach significantly enhances your resilience against ransomware, providing peace of mind as you navigate the digital landscape.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Now that you understand the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA), it’s time to implement it within your organization.
Start by assessing your current systems and identifying which applications and services could benefit most from MFA. Establish a clear plan that balances security and usability, ensuring all employees are trained on the new protocols.
As you roll out MFA, consider integrating it with existing security measures to enhance your overall defense strategy against threats like LockBit.
Best Practices for Setup
Multi-factor authentication is most effective when properly set up. Begin by selecting the right types of authentication methods for your organization, such as SMS codes, authenticator apps, or biometric scans.
Involve all users in the onboarding process by providing comprehensive training and clear instructions.
Regularly review your MFA settings and policies to adapt to any changes in your organization or emerging security threats, ensuring robust protection against unauthorized access.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
An often overlooked aspect of MFA is failing to enforce it consistently across all applications.
This creates vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Additionally, using single-factor authentication as a recovery method for MFA can compromise your security if your primary methods are breached.
You should also avoid relying solely on SMS-based codes, as these can be intercepted or spoofed. Ensuring that your MFA strategy is comprehensive and consistently applied will significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to attacks.
The most frequent pitfall in implementing MFA lies in inconsistent enforcement across applications and user groups.
Organizations sometimes roll out MFA to only a subset of critical systems, leaving gaps that attackers can exploit.
Furthermore, the use of weak backup methods, such as easily guessable questions or SMS codes, can undermine the security benefits of MFA.
Regular audits of your MFA processes and user compliance are crucial to avoid these issues and strengthen your cybersecurity posture against threats like LockBit.
Case Studies: Successful MFA Deployments
Despite the rising threat of LockBit attacks, organizations have successfully implemented Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance their cybersecurity. Studies include:
- Companies reduced unauthorized access incidents by 80% after deploying MFA across all user accounts.
- Some organizations experienced a 65% decrease in phishing attempts following MFA implementation.
- Some firms reported that 90% of users adopted MFA within the first month, resulting in a significant reduction in security breaches.
Real-World Examples
To illustrate the effectiveness of MFA, consider the case of the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) establishing comprehensive guidelines to ensure the protection of sensitive financial data and systems.
Among the key recommendations is the implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to bolster security measures against evolving cyber threats.
Lessons Learned from Implementation
Across various sectors, organizations have learned valuable lessons from MFA implementation, such as prioritizing user education and addressing common concerns regarding usability to encourage adoption.
Many have discovered that setting up MFA, though initially daunting, establishes a solid defense against cyber threats.
Implementation of MFA can often uncover unforeseen challenges such as user resistance or complexity in existing systems. You will find that providing clear guidance and support throughout the rollout process helps mitigate these issues.
#Moreover, ongoing education about the benefits of MFA reinforces user commitment and fosters a culture of security within your organization.
Future Trends in MFA and Cybersecurity
Keep an eye on the evolving landscape of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and cybersecurity.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, MFA will incorporate advanced technologies, including biometric solutions, machine learning, and AI-driven risk assessments, to adapt to new challenges.
These innovations will enhance your security posture and make it increasingly difficult for attackers to compromise your accounts.
Technological Advancements
At the forefront of security enhancement, technological advancements in MFA will automate the authentication process while maintaining strict security protocols.
Techniques such as passwordless authentication and behavioral biometrics are set to gain traction, allowing you to balance convenience and security effectively.
Continuous authentication will analyze your behavior in real time, making unauthorized access nearly impossible.
Predictions for Cyber Threats
Cybersecurity experts predict an increase in ransomware attacks leveraging sophisticated MFA evasion tactics.
As attackers refine their strategies, they may exploit vulnerabilities in existing authentication methods, making it important for you to stay vigilant.
The growing interconnectivity of devices is likely to open new avenues of attack, emphasizing the need for robust security protocols.
Consequently, your focus on proactive security measures will be vital in countering anticipated threats.
As ransomware tactics evolve, investing in adaptive and layered MFA strategies will help you navigate these complexities.
Regular training and awareness around emerging threats, alongside the integration of advanced technologies, will play a significant role in protecting your assets from future cyber-attacks.
Conclusion
Upon reflecting, you should recognize that implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is necessary for safeguarding your systems against LockBit attacks.
MFA adds a layer of security that significantly decreases the likelihood of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
By prioritizing MFA, you are taking proactive steps to protect your valuable information.
For more insights, check out this article on How to Reduce the Risk of LockBit Ransomware as a Victim.
FAQ
What is LockBit and how does it utilize vulnerabilities in security measures?
LockBit is a type of ransomware that targets organizations by encrypting their data and demanding a ransom for its release. It often exploits vulnerabilities in security measures, particularly when basic protection methods like passwords are used alone.
Cybercriminals often rely on compromised credentials to gain access to systems, which is where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) comes into play by adding an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to succeed with their plans.
How does Multi-Factor Authentication help in mitigating the risks associated with LockBit attacks?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly reduces the probability of an unauthorized access event leading to a LockBit attack.
By requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods such as something they know (password), something they have (a security token or smartphone app), or something they are (biometric data), organizations can create a robust barrier against attackers.
Even if a password is compromised, the additional authentication methods can thwart the attempts of cybercriminals to infiltrate systems and deploy ransomware.
What are some effective strategies to implement Multi-Factor Authentication in organizations?
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication effectively requires a few strategies:
- Comprehensive Policy: Develop a clear and thorough policy that outlines MFA requirements for all users and applications.
- User Training: Educate employees on the significance of MFA and how to use authentication tools properly, ensuring they understand its role in safeguarding the organization.
- Select Appropriate Authentication Methods: Choose authentication methods that align with your organization’s needs, such as SMS-based codes, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Periodically review your MFA implementation to ensure it remains effective against evolving threats and to confirm adherence to your policy across the organization.





