Table of Contents
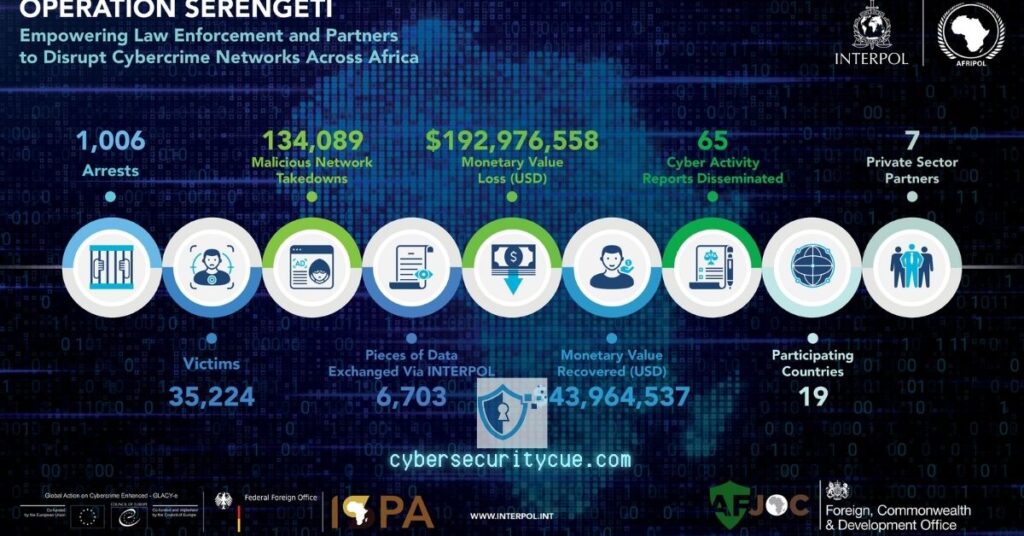
In a landmark operation against cybercrime, Interpol apprehended 1,006 suspects across Africa during Operation Serengeti, a two-month initiative targeting diverse online threats and scams.
From September 2 to October 31, this strategic move focused on dismantling ransomware schemes, online scams, and other malicious activities.
The operation uncovered nearly $193 million in reported losses, demonstrating the far-reaching impact of cybercriminal activities.
Key Takeaway:
- Interpol Cybercrime Arrests in Africa: Interpol’s Operation Serengeti shows the power of international collaboration, leading to 1,006 arrests and exposing $193 million in global cybercrime losses.
Scope and Duration of Interpol Cybercrime Arrests in Africa
Operation Serengeti was a coordinated effort by Interpol, running for two months to address cybercrimes such as business email compromise, ransomware, and digital extortion.
This initiative’s goal was clear: to identify and apprehend those responsible for online crimes affecting both individuals and organizations.
Highlights of the Operation:
- Timeline: September 2 – October 31, 2024
- Primary Focus: Online scams, ransomware attacks, and fraudulent activities
- Arrests Made: 1,006 suspects
By allocating significant resources to this initiative, Interpol emphasized the urgency of tackling cyber threats on the African continent.
Geographic Reach and Participation
Nineteen African nations joined forces for this operation, underscoring the need for international collaboration to counter cyber threats. Countries like Kenya, Senegal, and Nigeria played pivotal roles in identifying suspects and exposing criminal networks.
Participating Countries:
Algeria, Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Mauritius, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, South Africa, Tanzania, Tunisia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
This cross-border teamwork enhanced investigative capabilities and demonstrated a collective commitment to cyber safety.
This unprecedented level of engagement signifies a pivotal shift in how African nations approach cyber threats.
Total Arrests and Victims
This operation pinpointed about 35,000 victims affected by various forms of cybercrime, making it a significant step towards enhancing law enforcement capabilities in the region.
Financial Losses and Victim Impact
The financial ramifications of the crimes exposed during Operation Serengeti are staggering. Nearly $193 million in global losses were traced back to these schemes, affecting approximately 35,000 victims.
Notable Cases:
- Kenya: $8.6 million lost in a large-scale credit card fraud.
- Senegal: $6 million stolen through a Ponzi scheme involving five Chinese nationals.
These cases show how sophisticated scams have drained finances from victims, underlining the critical need for collaborative efforts in combating cybercrime.
Specific Arrests and Their Impact
With the successful execution of Operation Serengeti, numerous significant arrests have reshaped the landscape of cybercrime in Africa, and these arrests made during Operation Serengeti are reshaping Africa’s approach to cyber threats.
Among the notable cases:
- Kenya: Over 20 individuals apprehended in a credit card fraud operation.
- Senegal: Eight suspects, including five foreign nationals, arrested for orchestrating a Ponzi scheme.
- Cameroon: Multi-level marketing scams linked to human trafficking.
These arrests show how cybercrime intersects with other illegal activities, posing threats beyond financial losses.

Types of Scams and Crimes Targeted
With a focus on diverse cybercrimes, Operation Serengeti targeted various scams that have plagued individuals and businesses alike.
Interpol’s operation tackled a broad spectrum of cybercrimes. Some of the most common included:
| Type of Scam | Financial Impact |
|---|---|
| Online Ponzi Schemes | $6 million (Senegal) |
| Credit card fraud | $8.6 million (Kenya) |
| Multi-level Marketing Scams | Linked to human trafficking |
| Cryptocurrency Investment Scams | Major activity in Nigeria |
| Illegal Virtual Casinos | Run by international gangs (Angola) |
By addressing these crimes, Interpol has improved digital security and built stronger partnerships with local law enforcement.
After refining their strategies, law enforcement can proactively address the trends in cybercrime.
Plus, the operation’s results signal a shift in how countries are addressing cybercrime collectively, showing the importance of information sharing and international cooperation.
The targeted approach during Operation Serengeti has shown significant promise, placing a spotlight on the following areas of concern:
- Enhancing capabilities in cybercrime investigation
- Building stronger ties with private-sector tech firms
- Raising public awareness about cyber threats
- Increasing training for law enforcement agencies
- Focusing on technology-driven scams
After these advancements, you can expect continued vigilance from authorities to create a safer digital environment in Africa.
| Crime Focus | Operation Serengeti Result |
|---|---|
| Ransomware | Significant arrests |
| Business Email Compromise | Increased prevention strategies |
| Digital Extortion | Expanded law enforcement tactics |
| Online Scams | Heightened citizen awareness |
| Credit Card Fraud | Successful case resolutions |
Emerging Cybercrime Threats
The operation also revealed evolving cybercrime trends, including AI-driven malware and advanced phishing tactics. Criminals are adopting increasingly complex methods, emphasizing the need for constant vigilance and updated strategies from law enforcement agencies.
As highlighted by Interpol, criminals are continually evolving their tactics, leading to complex scams that impact society.
Interpol and Afripol: Strengthening Cybersecurity in Africa
Interpol, in collaboration with Afripol, played a pivotal role in equipping local law enforcement agencies with resources and training. These efforts are vital for combating cybercrime effectively and ensuring long-term digital security in Africa.
Key Takeaways from the Collaboration:
- Improved investigative capabilities.
- Increased international cooperation.
- Enhanced public awareness campaigns about cyber threats.
Overview of Interpol’s Operations
Operation Serengeti is one of Interpol‘s largest crackdowns on cybercrime in Africa. By working with local police and operational partners like Fortinet and Group-IB, the initiative not only made arrests but also strengthened Africa’s cyber defenses.
A Global Context: Comparing Law Enforcement Agencies
To understand Interpol’s unique role in addressing cybercrime, consider its operational scale compared to other agencies:
| Agency | Budget (Approx.) | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Interpol | €176 million | International collaboration on diverse crimes |
| Europol | €200 million+ | European financial and cybercrimes |
| FBI (USA) | $11 billion | Wide range, including terrorism and cybercrime |
Despite having a comparatively smaller budget, Interpol’s ability to coordinate global efforts is unparalleled.
This disparity can affect how swiftly and effectively justice is served, especially with the growing challenges posed by cybercriminals.
Operational partners:
Cybercrime Atlas, Fortinet, Group-IB, Kaspersky, Team Cymru, Trend Micro, Uppsala Security
Conclusion
Operation Serengeti marks a turning point in the fight against cybercrime in Africa. By arresting 1,006 suspects and exposing $193 million in losses, Interpol has sent a strong message to cybercriminals.
However, continued vigilance and cooperation are essential to build on this success and create a safer digital world.
FAQs About Interpol’s Cybercrime Arrests in Africa
What is Operation Serengeti?
Operation Serengeti is an Interpol-led initiative targeting cybercrime across Africa. Conducted over two months, it resulted in the arrest of 1,006 suspects involved in crimes like ransomware, online scams, and digital extortion, exposing $193 million in damages.
Which countries participated in the operation?
The operation involved 19 African countries, including Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, Senegal, Ghana, and Angola. This collaborative effort underscored the importance of cross-border coordination in tackling cyber threats.
What types of cybercrimes were targeted?
Interpol focused on a range of cybercrimes, including ransomware attacks, business email compromise, credit card fraud, Ponzi schemes, cryptocurrency scams, and multi-level marketing schemes linked to human trafficking.
How significant were the financial losses uncovered?
The operation revealed $193 million in losses globally, with notable cases like an $8.6 million credit card fraud in Kenya and a $6 million Ponzi scheme in Senegal. These figures highlight the financial and societal impact of cybercrime.
How many victims were identified during the operation?
Interpol identified approximately 35,000 victims of cybercrime across the participating countries. These victims were linked to scams ranging from online fraud to digital extortion schemes.
What was the role of Afripol in this operation?
Afripol collaborated with Interpol to enhance local law enforcement capabilities. The agency provided intelligence sharing, training, and operational support to address emerging cyber threats across African Union member states.
What are the key takeaways from Operation Serengeti?
The operation highlighted the importance of international collaboration, the need for enhanced cybercrime investigation skills, and the critical role of public-private partnerships. It also emphasized the growing sophistication of cybercriminals and the urgency of proactive countermeasures.





